Feynman Diagram: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "{{stub}} ==''Italic text'' Resources: == *[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Feynman_diagram Feynman diagram] *[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Compton_scattering Compton scatterin...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==''Italic text'' Resources: == | ==''Italic text'' Resources: == | ||
*[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Feynman_diagram Feynman diagram] | *[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Feynman_diagram Feynman diagram] | ||
| Line 23: | Line 21: | ||
*[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quantum_field_theory Quantum field theory] | *[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quantum_field_theory Quantum field theory] | ||
== Discussion: == | == Discussion: == | ||
{{stub}} | |||
Latest revision as of 22:19, 14 May 2023
Italic text Resources:[edit]
Discussion:[edit]
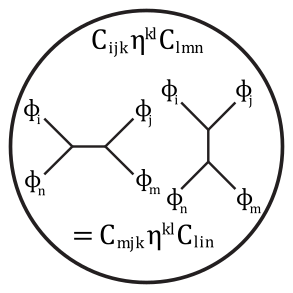
Richard Feynman (1918 - 1988)
Feynman diagram (1948) of Associativity in Quantum Field Theory
In theoretical physics, a Feynman diagram is a pictorial representation of the mathematical expressions describing the behavior and interaction of subatomic particles. The scheme is named after American physicist Richard Feynman, who introduced the diagrams in 1948. This particular diagram represents the Associative Property as expressed in Quantum Field Theory.