Fibonacci numbers: Difference between revisions
(Initial Stub) |
No edit summary |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
The beginning of the sequence is thus: | The beginning of the sequence is thus: | ||
:<math>0,\;1,\;1,\;2,\;3,\;5,\;8,\;13,\;21,\;34,\;55,\;89,\;144,\; \ldots</math> | :<math>0,\;1,\;1,\;2,\;3,\;5,\;8,\;13,\;21,\;34,\;55,\;89,\;144,\; \ldots</math> | ||
Fibonacci numbers are named after Italian mathematician Leonardo of Pisa, later known as Fibonacci. In his 1202 book Liber Abaci, Fibonacci introduced the sequence to Western European mathematics, although the sequence had been described earlier in Indian mathematics as early as 200 BC in work by Pingala on enumerating possible patterns of Sanskrit poetry formed from syllables of two lengths. | |||
==Mathematics== | |||
The ratio <math> \frac {F_n}{F_{n+1}} \ </math> approaches the golden ratio as <math>n</math> approaches infinity. | |||
[[File:PascalTriangleFibanacci.png|thumb|right|360px|The Fibonacci numbers are the sums of the "shallow" diagonals (shown in red) of Pascal's triangle.]] | |||
The Fibonacci numbers occur in the sums of "shallow" diagonals in Pascal's triangle. | |||
:<math>F_n = \sum_{k=0}^{\left\lfloor\frac{n-1}{2}\right\rfloor} \binom{n-k-1}{k}</math> | |||
Counting the number of ways of writing a given number <math>n</math> as an ordered sum of 1s and 2s (called compositions); there are <math>F_{n+1}</math> ways to do this. For example, if <math>n = 5</math>, then <math>F_{n+1} = F_{6} = 8</math> counts the eight compositions summing to 5: | |||
<math>1+1+1+1+1 = 1+1+1+2 = 1+1+2+1 = 1+2+1+1 = 2+1+1+1 = 2+2+1 = 2+1+2 = 1+2+2</math> | |||
== Resources: == | == Resources: == | ||
| Line 16: | Line 28: | ||
*[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fibonacci_number Fibonacci numbers] | *[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fibonacci_number Fibonacci numbers] | ||
== Discussion: == | == Discussion: == | ||
[[Category:Pages for Merging]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:49, 19 February 2023
In mathematics, the Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted [math]\displaystyle{ F_n }[/math], form a sequence, called the Fibonacci sequence, such that each number is the sum of the two preceding ones, starting from 0 and 1. That is,
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_0=0,\quad F_1= 1, }[/math]
and
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_n=F_{n-1} + F_{n-2}, }[/math]
for [math]\displaystyle{ n \gt 1 }[/math].
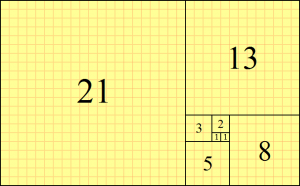
The beginning of the sequence is thus:
- [math]\displaystyle{ 0,\;1,\;1,\;2,\;3,\;5,\;8,\;13,\;21,\;34,\;55,\;89,\;144,\; \ldots }[/math]
Fibonacci numbers are named after Italian mathematician Leonardo of Pisa, later known as Fibonacci. In his 1202 book Liber Abaci, Fibonacci introduced the sequence to Western European mathematics, although the sequence had been described earlier in Indian mathematics as early as 200 BC in work by Pingala on enumerating possible patterns of Sanskrit poetry formed from syllables of two lengths.
MathematicsEdit
The ratio [math]\displaystyle{ \frac {F_n}{F_{n+1}} \ }[/math] approaches the golden ratio as [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] approaches infinity.
The Fibonacci numbers occur in the sums of "shallow" diagonals in Pascal's triangle.
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_n = \sum_{k=0}^{\left\lfloor\frac{n-1}{2}\right\rfloor} \binom{n-k-1}{k} }[/math]
Counting the number of ways of writing a given number [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] as an ordered sum of 1s and 2s (called compositions); there are [math]\displaystyle{ F_{n+1} }[/math] ways to do this. For example, if [math]\displaystyle{ n = 5 }[/math], then [math]\displaystyle{ F_{n+1} = F_{6} = 8 }[/math] counts the eight compositions summing to 5:
[math]\displaystyle{ 1+1+1+1+1 = 1+1+1+2 = 1+1+2+1 = 1+2+1+1 = 2+1+1+1 = 2+2+1 = 2+1+2 = 1+2+2 }[/math]