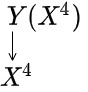Observerse: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The '''observerse''' is the central mathematical object in the [[Theory of Geometric Unity]]. It is a mapping from a four-dimensional manifold | The '''observerse''' is the central mathematical object in the [[Theory of Geometric Unity]]. It is a mapping from a four-dimensional manifold <math>X^4<\math> to a manifold <math>Y</math>, which replaces Einstein's spacetime. There are four different constructions of the observerse: exogenous, bundle-theoretic, endogenous, and tautological. Each generates a possible Geometric Unity theory. | ||
== Exogenous == | == Exogenous == | ||
In the observerse's exogenous construction, the manifold | In the observerse's exogenous construction, the manifold <math>X^4</math> includes into any manifold <math>Y</math> of four dimensions or higher which can admit it as an immersion. | ||
<math> X^4 \hookrightarrow Y </math> | |||
== Bundle-Theoretic == | == Bundle-Theoretic == | ||
In the observerse's bundle-theoretic construction, the manifold | In the observerse's bundle-theoretic construction, the manifold <math>Y</math> sits over <math>X^4</math> as a fiber bundle. | ||
[[File:Observerse-Bundle-Theoretic.jpg]] | [[File:Observerse-Bundle-Theoretic.jpg]] | ||
== Endogenous == | == Endogenous == | ||
In the observerse's endogenous construction, | In the observerse's endogenous construction, <math>Y</math> is the space of metrics on the manifold <math>X^4</math>. | ||
[[File:Observerse-Endogenous.jpg]] | [[File:Observerse-Endogenous.jpg]] | ||
== Tautological == | == Tautological == | ||
In the observerse's tautological construction, the manifold | In the observerse's tautological construction, the manifold <math>X^4</math> equals <math>Y</math>. | ||
<math> X^4 = Y </math> | |||
[[Category:Geometric Unity]] | [[Category:Geometric Unity]] | ||
[[Category:Ericisms]] | [[Category:Ericisms]] | ||
Revision as of 16:43, 19 February 2023
The observerse is the central mathematical object in the Theory of Geometric Unity. It is a mapping from a four-dimensional manifold [math]\displaystyle{ X^4\lt \math\gt to a manifold \lt math\gt Y }[/math], which replaces Einstein's spacetime. There are four different constructions of the observerse: exogenous, bundle-theoretic, endogenous, and tautological. Each generates a possible Geometric Unity theory.
Exogenous
In the observerse's exogenous construction, the manifold [math]\displaystyle{ X^4 }[/math] includes into any manifold [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] of four dimensions or higher which can admit it as an immersion.
[math]\displaystyle{ X^4 \hookrightarrow Y }[/math]
Bundle-Theoretic
In the observerse's bundle-theoretic construction, the manifold [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] sits over [math]\displaystyle{ X^4 }[/math] as a fiber bundle.
Endogenous
In the observerse's endogenous construction, [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] is the space of metrics on the manifold [math]\displaystyle{ X^4 }[/math].
Tautological
In the observerse's tautological construction, the manifold [math]\displaystyle{ X^4 }[/math] equals [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math].
[math]\displaystyle{ X^4 = Y }[/math]